Food waste, a staggering global issue, poses an immense threat to our planet’s delicate ecosystems and sustainable future. Each year, billions of tons of food are discarded, squandering not only precious resources but also contributing to various environmental, economic, and social challenges. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the deeply concerning harmful effects of food waste on our planet and explore practical ways individuals can actively combat this pressing problem.
The impact of Food waste on our environment
Environmental Consequences of Food Waste
Food waste has far-reaching environmental implications that extend beyond our immediate surroundings.
Climate Change
At the forefront of the environmental impact of food waste is its significant contribution to climate change. When food scraps decompose in landfills, they produce copious amounts of methane, a potent greenhouse gas that traps heat in the atmosphere. Methane is considerably more damaging than carbon dioxide, exacerbating the greenhouse effect and accelerating global warming. By minimizing food waste, we can substantially reduce methane emissions and play a vital role in mitigating climate change.
Water Resources
Food production demands extensive water resources. However, a considerable portion of this water is squandered when food goes to waste. As water scarcity intensifies in many regions worldwide, minimizing food waste becomes an essential measure to conserve this invaluable resource.
Land Use and Deforestation
To meet the escalating demand for food, vast areas of land are cleared for agricultural purposes, leading to deforestation and the destruction of natural habitats. By reducing food waste, we can alleviate the pressure on expanding agricultural lands and contribute to preserving precious ecosystems.
Biodiversity Loss
The expansion of agricultural lands and the use of harmful chemicals in food production lead to biodiversity loss, threatening numerous plant and animal species. By cutting down on food waste, we can decrease the demand for intensive farming practices and foster biodiversity conservation.
Food Production and Distribution
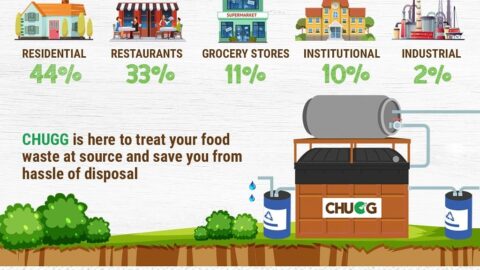
Food waste occurs not only at the consumer level but also during production and distribution. Crop losses due to pests and diseases, spoilage during transportation, and stringent cosmetic standards contribute to a significant amount of food wasted even before reaching the market. Addressing these inefficiencies in the supply chain is critical to minimizing overall food waste.
Economic Implications
Beyond its environmental consequences, food waste has substantial economic ramifications. Wastage throughout the food supply chain translates into financial losses at every stage, from producers and distributors to consumers. By addressing food waste, we can create a more economically sustainable food system and reduce financial burdens.
Social Consequences
While food waste plagues many developed countries, it starkly contrasts with the issue of food insecurity prevalent in various parts of the world. Surplus food that could have fed the hungry ends up discarded in landfills. By reducing food waste and redirecting excess food to those in need, we can make a significant impact on alleviating food insecurity and hunger.
The Role of Individuals minimizing Food Waste reaching the landfills
While addressing food waste requires collective action from governments, businesses, and communities, individuals play a crucial role in making a tangible difference.
1 Composting
Composting is a sustainable and eco-friendly method to dispose of food scraps. By turning food waste into nutrient-rich compost, individuals can contribute to healthier soils, support sustainable agriculture, and reduce methane emissions from landfills.
2 Donating
Rather than throwing away excess food, consider donating it to local food banks or shelters. Donations ensure that edible food reaches those who need it most, combating food waste while also helping vulnerable communities.
3 Meal Planning
Effective meal planning is a proactive approach to reducing food waste at the household level. By carefully planning meals and creating shopping lists, individuals can purchase only what they need, reducing the likelihood of food going to waste.
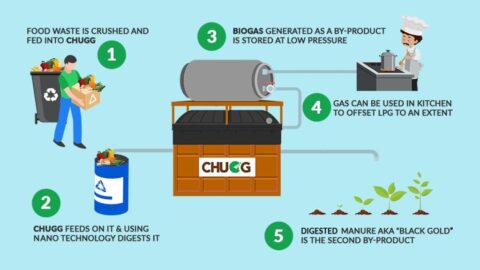
4 CHUGG
The CHUGG Food Waste Treatment System offers a promising solution to address the harmful effects of food waste on our planet and contributes significantly to mitigating the climate crisis. This innovative system, provided by Avris Technologies, utilizes biogas technology as a sustainable approach to manage food waste efficiently and minimize its environmental impact.
1. Biogas Production and Methane Emissions Reduction:
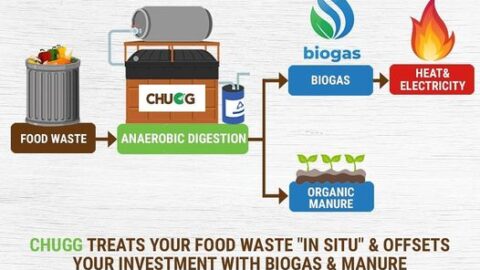
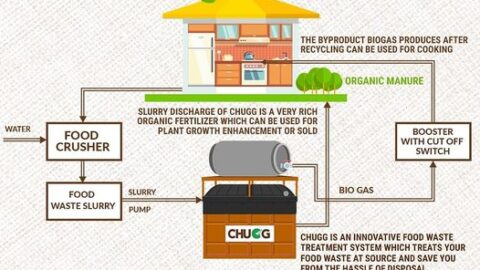
One of the key features of the CHUGG Food Waste Treatment System is its ability to convert food waste into biogas through a process known as anaerobic digestion. Anaerobic digestion breaks down organic matter in the absence of oxygen, producing biogas as a byproduct. Biogas mainly consists of methane, which is a potent greenhouse gas with a significantly higher global warming potential than carbon dioxide. Instead of allowing food waste to decompose in landfills and emit methane directly into the atmosphere, the CHUGG system captures this methane during anaerobic digestion. By doing so, it helps reduce methane emissions, which is a crucial step in combating climate change.
2. Renewable Energy Generation:
The biogas produced in the CHUGG Food Waste Treatment System is not only an effective way to tackle methane emissions but also a valuable source of renewable energy. This biogas can be harnessed and utilized as a clean and sustainable energy resource. It can power generators to produce electricity, heat buildings, or fuel vehicles, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and further mitigating greenhouse gas emissions associated with traditional energy sources.
3. Nutrient-Rich Digestate and Soil Health Improvement:
Apart from generating biogas, the CHUGG system also produces a nutrient-rich byproduct called digestate. This digestate can serve as an organic fertilizer with high nutrient content. When applied to agricultural fields, it enhances soil health, fertility, and water retention, thereby contributing to sustainable agriculture practices and reducing the need for chemical fertilizers.
4. Waste Diversion and Landfill Reduction:
By implementing the CHUGG Food Waste Treatment System, large amounts of food waste that would have otherwise ended up in landfills are diverted and processed more sustainably. This reduces the burden on landfills, which are significant sources of methane emissions. Landfill diversion also promotes a circular economy approach, where food waste is repurposed into valuable resources, reducing overall waste generation and its detrimental impact on the environment.
5. Contribution to Circular Economy and Sustainable Practices:
The CHUGG system exemplifies the principles of the circular economy by effectively closing the loop on food waste. Instead of viewing food waste as a problem to be disposed of, the system transforms it into useful products, such as biogas and organic fertilizer. This approach aligns with broader sustainable practices, emphasizing resource efficiency and minimizing negative environmental impacts.
Conclusion
The harmful effects of food waste on our planet are undeniable, affecting the environment, economy, and society. It is imperative for us to understand the gravity of this issue and take action to address it. By embracing sustainable practices, minimizing food waste, and making conscious choices, we can collectively create a brighter, more sustainable future for our planet and its inhabitants.
The CHUGG
Learn how CHUGG converts food waste into renewable energy and nutrient-rich fertilizer, while combating climate change and promoting a circular economy. is an innovative technology that directly addresses the harmful effects of food waste on our planet. By converting food waste into valuable biogas, producing renewable energy, enriching soils, and reducing landfill contributions, this system plays a significant role in combating climate change and fostering a more sustainable future. It stands as a promising example of how innovative biogas technology can be an effective tool in the battle against the detrimental consequences of food waste on our delicate ecosystems and the broader global climate.