Introduction
In an era marked by mounting environmental concerns and the imperative to manage resources judiciously, the discourse around food waste and food loss has reached a crescendo. The intricacies of these concepts are not merely linguistic nuances but embody a profound distinction in the context of resource utilization and sustainability. This article undertakes a comprehensive journey to illuminate the differences between food waste and food loss while elucidating innovative measures, particularly the groundbreaking CHUGG food waste treatment system, that can be employed to confront these challenges.
Unpacking the Essence of Food Waste and Food Loss
Defining the Parameters
Delineating food waste from food loss requires a nuanced understanding. Food waste encompasses the discard of edible components due to a myriad of factors, including spoilage, excess procurement, and inadvertence. On the contrary, food loss encapsulates the non-delivery of food to its intended destination due to logistical hurdles, sub-optimal storage, and inefficiencies within the supply chain.
The Global Spectrum of the Issue
The global magnitude of food waste and food loss is staggering and merits immediate attention. Shockingly, the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) estimates that approximately one-third of all food produced globally meets a wasteful fate. This has severe ramifications, extending beyond the economic realm to encompass social repercussions and environmental ramifications, exacerbating food security concerns and intensifying the ramifications of climate change.
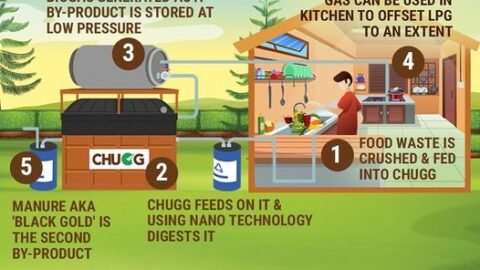
The Trailblazing CHUGG Food Waste Treatment System
Genesis of the CHUGG System
Amidst this labyrinth of food wastage and loss, the CHUGG food waste treatment system emerges as a veritable beacon of hope. This innovative system harnesses the power of anaerobic digestion, a natural biological process, to metamorphose organic waste into two invaluable resources: biogas and nutrient-enriched fertilizer.
Deciphering the Anaerobic Digestion Process
The core of the CHUGG system lies in the process of anaerobic digestion, a chemical reaction where organic substances undergo decomposition in an oxygen-deprived milieu. Within the confines of the CHUGG system, microorganisms toil diligently, breaking down food waste and expelling biogas, a renewable energy source, while simultaneously engendering nutrient-rich fertilizer that can bolster agricultural productivity.
Multi-Faceted Gains of the CHUGG System
The CHUGG system extends an assortment of advantages that reverberate on multiple fronts:
Mitigation of Methane Emissions: By facilitating anaerobic digestion, the CHUGG system mitigates the release of methane, an insidious greenhouse gas known for its role in climate change.
Sustainable Energy Production: The biogas engendered through this process serves as a cogent alternative to fossil fuels, aligning with renewable energy objectives.
Harbinger of the Circular Economy: The ethos of the CHUGG system underscores the principles of a circular economy, transmuting waste into invaluable resources, fostering resource efficiency, and diminishing waste’s ecological footprint.
Navigating Implementation Hurdles with Ingenuity
Undoubtedly, the CHUGG system presents a trans-formative potential; however, its adoption is not devoid of challenges. Initial expenses and requisite infrastructure pose as notable barriers. Yet, governments, corporate entities, and communities can orchestrate synergistic efforts to surmount these hurdles. Collaborative investments, incentive adoption, and a supportive legislative framework can pave the way for widespread acceptance.
Orchestrating a Symphony of Strategies Against Food Waste and Loss
Fortifying Consumer Awareness
Consumer education stands as a pivotal instrument in orchestrating a paradigm shift. Enlightening individuals about prudent purchasing practices, optimal storage methodologies, and the ecological implications of food waste can usher in a culture of conscious consumption.
Enhancing the Resilience of Supply Chains
Strengthening supply chains is pivotal in mitigating food loss. Enhanced logistics, improved storage mechanisms, and streamlined distribution channels can ensure that a larger quantum of food reaches its designated recipients.
Convergence of Stakeholder Efforts
The fabric of change is woven through cohesive collaboration. The magnitude of the food waste predicament necessitates a collaborative front comprising governments, corporate players, agrarians, and end consumers. Unified endeavors can give rise to innovative policies, sustainable technologies, and cohesive strategies that encompass the entire spectrum of food waste.
Conclusion
In a world poised at the brink of resource exhaustion and grappling with the specter of climate change, the issue of food waste and food loss assumes paramount importance. Discerning the nuances between these terminologies and embracing avant-garde solutions like the CHUGG food waste treatment system can engender a seismic shift towards a more sustainable trajectory. Through collective vigilance, we possess the potential to curtail waste, preserve precious resources, and safeguard the planet for future generations.