Food waste is a pressing issue in India, where millions of tons of food are discarded each year while millions of people go hungry. To combat this problem, individuals, communities, and businesses must come together to adopt effective measures that can significantly reduce food waste. In this detailed article, we will explore various strategies and initiatives aimed at managing food waste in India. Food waste is a global problem, but in India, the challenge is particularly daunting. With a growing population and an unequal distribution of resources, it is crucial to address the issue of food waste effectively. This article will delve into various strategies and initiatives that can help manage food waste in India.
Understanding the Scale of the Problem
Food waste in India is not a trivial matter. It is estimated that nearly 40% of the food produced in the country goes to waste. To tackle this issue, we must first understand the extent of the problem.
The Role of Consumer Awareness
1. Raising Awareness About Food Expiry Dates: One of the primary causes of food waste at the consumer level is the misunderstanding of food expiry dates. Many people discard food prematurely, believing it to be unsafe, when it is still perfectly edible. Educating consumers about these dates is crucial. Food expiration dates are often misunderstood. In many cases, food is discarded prematurely because consumers misinterpret these dates as indicators of spoilage or safety. To combat this issue, it’s essential to educate consumers about the meaning of these dates. Food items often have “best before” or “use by” dates, which suggest the peak quality of the product, not its safety.
2. Educating Consumers About Portion Control: Consumers often serve themselves more than they can eat, leading to leftover food that eventually goes to waste. Promoting portion control can significantly reduce food waste in households. Portion control is another critical aspect of reducing food waste. Many individuals tend to serve themselves larger portions than they can consume, resulting in leftover food that often ends up being thrown away. By educating consumers about portion control and encouraging them to serve smaller portions, we can minimize food waste at the source.
2. Effective Food Storage Techniques
Proper food storage is essential to prolong the shelf life of perishable items. Several techniques can be employed to achieve this goal.
- Airtight Containers and Refrigeration: Investing in airtight containers and refrigerating perishable items can prevent them from spoiling prematurely. Airtight containers are an effective way to store various food items, particularly those that are prone to spoilage or moisture absorption. These containers create a sealed environment that helps maintain the freshness of the contents. For example, grains, cereals, and spices can be stored in airtight containers to prevent them from losing flavor and becoming infested with pests. Refrigeration plays a crucial role in extending the shelf life of perishable items such as fruits, vegetables, dairy products, and meats. Cold temperatures slow down the growth of bacteria and other microorganisms that cause food to spoil. Additionally, storing food in the right compartments of the refrigerator can further enhance its freshness. For example, fruits and vegetables should be stored in separate drawers with humidity controls to maintain their crispness and prevent wilting.
- FIFO Method: The “First In, First Out” method encourages using older products before newer ones to ensure nothing expires unused. The “First In, First Out” (FIFO) method is a simple yet effective strategy for reducing food waste at home. It involves organizing your pantry, refrigerator, and freezer in a way that ensures older food items are used before newer ones. When you buy groceries or cook meals, make an effort to reach for the items with the earliest expiration or use-by dates. This practice helps prevent food from languishing at the back of your storage spaces and going to waste.
- Root Cellars: Traditional root cellars can provide a cool, dark, and humidity-controlled environment for storing fruits and vegetables, extending their freshness.Root cellars are time-tested storage solutions, especially in regions where seasonal variations in temperature occur. These underground or partially buried structures provide a stable, cool, and dark environment with controlled humidity levels. Root cellars are particularly effective for extending the shelf life of fruits and vegetables, making them less susceptible to spoilage and ensuring a steady supply of fresh produce.
3. Supporting Local Food Banks
Donating excess food to local food banks can help ensure that surplus food reaches those in need instead of ending up in landfills. Supporting local food banks is a meaningful way to reduce food waste and contribute to the well-being of the community. When you have excess food that you cannot consume or do not plan to use, consider donating it to a local food bank or shelter. Many organizations have networks in place to collect and distribute surplus food to individuals and families facing food insecurity.
4. Promoting Food Donation Drives
Organizing food donation drives in communities can be a powerful way to channel excess food to those who require it most. Food donation drives are community-based initiatives that actively involve individuals, businesses, and organizations in the process of reducing food waste and addressing hunger. These drives can take various forms, from collecting surplus food at local events to coordinating regular food drives within neighborhoods. By encouraging participation in such drives, we can bridge the gap between excess food and those in need.
5. Encouraging Responsible Shopping
Responsible shopping habits can significantly reduce food waste from the outset.
- Make Shopping Lists: Creating shopping lists before heading to the store helps buyers stick to what they need, reducing impulse purchases that often lead to waste. One of the most effective ways to curb food waste begins before you even leave for the grocery store. Making a shopping list can be a game-changer. By planning your purchases in advance and sticking to your list, you’re less likely to buy items on a whim or in excess. This simple practice not only saves money but also helps reduce food waste at home.
- Avoid Impulse Buying: Resisting the temptation to make impulse buys can prevent unnecessary food items from piling up. Impulse buying is a common behavior that often results in food waste. Those unplanned purchases may seem enticing at the moment, but they can lead to items sitting in your pantry or refrigerator until they expire. Before adding something to your cart, pause and ask yourself if it’s a necessary item that you will use in the near future. This practice can help you avoid accumulating items that end up going to waste.
- Buy Imperfect Produce: Supporting the purchase of imperfect or “ugly” produce can reduce waste, as these items are often discarded by retailers despite being perfectly good to eat. “Ugly” or imperfect produce refers to fruits and vegetables that don’t meet the cosmetic standards set by retailers. These items may have blemishes, irregular shapes, or other imperfections that do not affect their taste or nutritional value. However, they are often discarded by stores, contributing to food waste. By choosing to buy imperfect produce, you not only reduce food waste but also support sustainable farming practices.
6. Innovations in Food Packaging
Innovations in food packaging can play a vital role in reducing food waste.
1. Biodegradable Packaging: The adoption of biodegradable packaging materials can reduce the environmental impact of food packaging waste. Biodegradable packaging materials are designed to break down naturally over time, reducing the environmental footprint of packaging waste. Unlike traditional plastic packaging, which can persist in landfills for centuries, biodegradable materials decompose more rapidly, returning nutrients to the soil. By choosing products packaged in biodegradable materials, consumers can contribute to a more sustainable and eco-friendly approach to food packaging.
2. Smart Packaging Labels: Smart labels that indicate the freshness of a product can help consumers make informed choices and use items before they spoil. Smart packaging labels incorporate technology to provide real-time information about the freshness and safety of food products. These labels may use color-changing indicators, QR codes, or RFID tags to convey information to consumers. By scanning or observing these labels, shoppers can determine whether a product is still safe to consume. This technology empowers consumers to make informed decisions and reduces the likelihood of prematurely discarding food that is still perfectly good.
7. Community Composting Initiatives
Setting up community compost bins and conducting composting workshops can educate people about the benefits of composting and divert organic waste from landfills. Community composting initiatives are grassroots efforts that aim to reduce food waste by diverting organic materials from landfills and turning them into nutrient-rich compost. Compost bins are often placed in accessible locations within neighborhoods, making it convenient for residents to participate. Additionally, composting workshops and educational programs help individuals understand the composting process and encourage them to participate actively.
8. Government Policies and Regulations
Government intervention is essential in addressing food waste on a larger scale.
1. The Need for Stringent Food Waste Laws: Implementing strict regulations regarding food waste disposal and penalties for non-compliance can encourage responsible practices. Government policies and regulations play a significant role in shaping how food waste is managed at various levels. One critical step is the implementation of stringent food waste laws that outline clear guidelines for the disposal of food waste. These laws can establish penalties for non-compliance, encouraging businesses and individuals to adopt responsible practices. Additionally, such regulations may require businesses to report on their food waste reduction efforts, promoting transparency and accountability.
2. Tax Incentives for Food Donation: Offering tax incentives to businesses and individuals who donate excess food can stimulate food donation efforts. Tax incentives are powerful tools for encouraging food donation. Governments can offer tax deductions or credits to businesses and individuals that donate surplus food to registered charities or food banks. These incentives not only reduce the financial burden on donors but also promote a culture of food sharing and philanthropy. By rewarding food donation, governments can further incentive responsible food management practices.
9. Technological Solutions
In the digital age, technology plays a pivotal role in addressing food waste challenges in India. Various innovative solutions harness the power of technology to reduce food waste, enhance efficiency, and facilitate better food management practices.
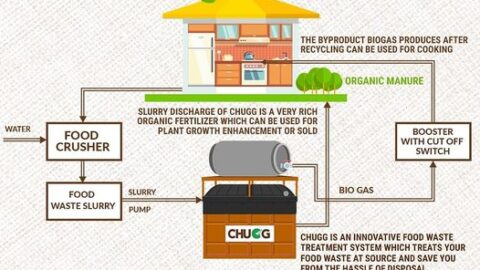
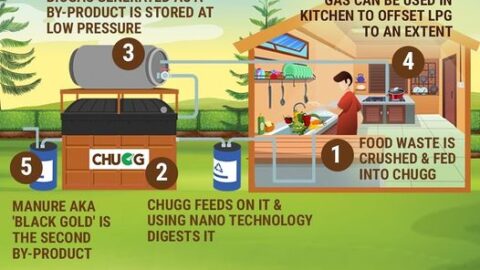
- The CHUGG- IN SITU FOOD WASTE TREATMENT SYSTEM is a cutting-edge technological solution designed to tackle food waste at its source. This system offers an on-site, in-house food waste treatment process that efficiently breaks down organic food waste, including kitchen scraps and leftovers, into reusable byproducts. One of the primary advantages of the CHUGG system is its ability to minimize food waste collection and transportation, reducing the carbon footprint associated with traditional waste disposal methods. By implementing this technology, restaurants, hotels, and large food service establishments can significantly reduce food waste volume, cut disposal costs, and contribute to a more sustainable approach to food management. To Know more Visit https://www.avristech.com/food-waste-treatment-system/
- Food Waste Apps: Mobile apps that connect consumers with food donation centers and provide tips on reducing food waste can make a significant impact. Food waste apps leverage technology to address food waste challenges. These mobile applications connect consumers, restaurants, and grocery stores with food donation centers or individuals in need. Users can easily donate surplus food or find nearby locations where excess food is available for collection. Additionally, these apps often offer tips and guidance on reducing food waste at home, making them valuable resources for individuals and businesses alike.
- IoT Sensors in Food Storage: Internet of Things (IoT) sensors can monitor food storage conditions and send alerts when items are approaching their expiry dates. The Internet of Things (IoT) has revolutionized food storage and management. IoT sensors placed in refrigerators, pantries, and warehouses can continuously monitor the conditions of stored food items. These sensors can detect temperature fluctuations, humidity levels, and even track expiration dates. When an item is approaching its use-by date or when storage conditions are sub-optimal, the sensor can send alerts to users’ smartphones, helping them use or donate the item before it spoils.
10 Reducing Food Waste in Restaurants
Restaurants can also play a crucial role in minimizing food waste.
- Smaller Portions and Half Portions: Offering smaller portion sizes and half portions on the menu can reduce plate waste in restaurants. Restaurants often serve portions that are larger than what many diners can comfortably consume. This practice results in uneaten food being sent to the kitchen as plate waste. To combat this issue, some restaurants have started offering smaller portion sizes or half portions on their menus. This not only reduces food waste but also allows diners to enjoy a variety of dishes without feeling obligated to overindulge.
- Creative Menu Planning: Restaurants can design menus that utilize ingredients efficiently, reducing the chances of food going to waste. Creative menu planning is essential for restaurants looking to minimize food waste. Chefs and kitchen staff can collaborate to design menus that use ingredients efficiently. For example, a dish might incorporate multiple components that can be repurposed in different menu items. Additionally, seasonal and locally sourced ingredients can be prioritized to reduce food spoilage and waste.
11. No Food Waste Campaign
The No Food Waste campaign in Chennai has been successful in collecting excess food from events and distributing it to the hungry. The No Food Waste campaign, based in Chennai, India, has made significant strides in food waste reduction. This initiative actively collects excess food from events, restaurants, and individuals and redistributes it to people facing food insecurity. By preventing edible food from going to waste and channeling it to those in need, the campaign exemplifies the positive impact of community-driven food waste reduction efforts.
Conclusion
Managing food waste in India is a complex but essential task. By raising consumer awareness, improving food storage practices, supporting food banks, and implementing technological solutions, we can make significant strides in reducing food waste and ensuring that more people have access to the food they need. Technological solutions such as the CHUGG- IN SITU FOOD WASTE TREATMENT SYSTEM, food waste apps, and IoT sensors offer valuable assistance in the battle against food waste in India. These innovations promote transparency, efficiency, and accountability while actively engaging individuals and businesses in reducing food waste at all levels of the food supply chain.